 Gatheright bought sweet potatoes from Clark, paying with two post-dated checks. When they were returned for insufficient funds, Clark instituted criminal proceedings against Gatheright, which were ultimately dismissed after Gatheright spent several weeks in jail. Gatheright then sued Clark for malicious prosecution and abuse of process. The Fifth Circuit affirmed summary judgment for Clark, observing that “$16,000 in bad checks . . . [is] a sum greater than what the Mississippi Supreme Court has previously found would prompt a reasonable person to institute criminal proceedings.” Based on that observation, the Court rejected arguments about whether a post-dated
Gatheright bought sweet potatoes from Clark, paying with two post-dated checks. When they were returned for insufficient funds, Clark instituted criminal proceedings against Gatheright, which were ultimately dismissed after Gatheright spent several weeks in jail. Gatheright then sued Clark for malicious prosecution and abuse of process. The Fifth Circuit affirmed summary judgment for Clark, observing that “$16,000 in bad checks . . . [is] a sum greater than what the Mississippi Supreme Court has previously found would prompt a reasonable person to institute criminal proceedings.” Based on that observation, the Court rejected arguments about whether a post-dated  check was a proper basis for a “false pretenses” prosecution in Mississippi, and about the effect of Gatheright’s filing for personal bankruptcy. Gatheright v. Clark, No. 16-60364 (Feb. 23, 2017, unpublished).
check was a proper basis for a “false pretenses” prosecution in Mississippi, and about the effect of Gatheright’s filing for personal bankruptcy. Gatheright v. Clark, No. 16-60364 (Feb. 23, 2017, unpublished).
Monthly Archives: February 2017
 It is well-settled nationally that “an appellate court may not alter a judgment to benefit a nonappealing party” because “it takes a cross-appeal to justify a remedy in favor of an appellee.” Greenlaw v. United States, 554 U.S. 237, 244–45 (2008). The Fifth Circuit treats that principle as jurisdictional. See, e.g., Amazing Spaces, Inc. v. Metro Mini Storage, 608 F.3d 225, 250 (5th Cir. 2010) (“[T]his circuit follows the general rule that, in the absence of a cross-appeal, an appellate court has no jurisdiction to modify a judgment so as to enlarge the rights of the appellee or diminish the rights of the appellant.”) Some other Circuits, however, take a different view. See, e.g., Am. Roll-On Roll-Off Carrier LLC v. P&O Parts Baltimore, Inc., 479 F.3d 288, 295 (4th Cir. 2007) (“This circuit views the cross-appeal requirement as one of practice, rather than as a strict jurisdictional requirement.”) (Thanks to my LPCH colleague Russ Herman for pointing this out.)
It is well-settled nationally that “an appellate court may not alter a judgment to benefit a nonappealing party” because “it takes a cross-appeal to justify a remedy in favor of an appellee.” Greenlaw v. United States, 554 U.S. 237, 244–45 (2008). The Fifth Circuit treats that principle as jurisdictional. See, e.g., Amazing Spaces, Inc. v. Metro Mini Storage, 608 F.3d 225, 250 (5th Cir. 2010) (“[T]his circuit follows the general rule that, in the absence of a cross-appeal, an appellate court has no jurisdiction to modify a judgment so as to enlarge the rights of the appellee or diminish the rights of the appellant.”) Some other Circuits, however, take a different view. See, e.g., Am. Roll-On Roll-Off Carrier LLC v. P&O Parts Baltimore, Inc., 479 F.3d 288, 295 (4th Cir. 2007) (“This circuit views the cross-appeal requirement as one of practice, rather than as a strict jurisdictional requirement.”) (Thanks to my LPCH colleague Russ Herman for pointing this out.)
 Recipients of Section 8 housing assistance sued mortgage originators, complaining that the originators either denied or discouraged the recipients’ credit applications by not considering their Section 8 income, in violation of the Equal Credit Opportunity Act. The Fifth Circuit affirmed the dismissal of claims by recipients who had only inquired about, rather than actually starting, the application process, as well as claims based on Wells Fargo’s policies about the purchase of mortgages in the secondary market. It reversed as to one group of applicants, however, finding under Iqbal and the substantive law that they “plausibly alleged that AmeriPro refused to consider their Section 8 income in assessing their creditworthiness as mortgage applicants, and that they received mortgages on less favorable terms and in lesser amounts than they would have had their Section 8 income been considered.” Alexander v. AmeriPro, No. 15-20710 (Feb. 16, 2017).
Recipients of Section 8 housing assistance sued mortgage originators, complaining that the originators either denied or discouraged the recipients’ credit applications by not considering their Section 8 income, in violation of the Equal Credit Opportunity Act. The Fifth Circuit affirmed the dismissal of claims by recipients who had only inquired about, rather than actually starting, the application process, as well as claims based on Wells Fargo’s policies about the purchase of mortgages in the secondary market. It reversed as to one group of applicants, however, finding under Iqbal and the substantive law that they “plausibly alleged that AmeriPro refused to consider their Section 8 income in assessing their creditworthiness as mortgage applicants, and that they received mortgages on less favorable terms and in lesser amounts than they would have had their Section 8 income been considered.” Alexander v. AmeriPro, No. 15-20710 (Feb. 16, 2017).
 I commented today on Dallas’s Fox 4 News about how the potential deployment of the National Guard about illegal immigration could implicate the Posse Comitatus Act.
I commented today on Dallas’s Fox 4 News about how the potential deployment of the National Guard about illegal immigration could implicate the Posse Comitatus Act.
Just before filing for bankruptcy, Mr. Wiggins signed a “Partition Agreement” in which he and his wife divided their ownership of their home into two separate property interests. The Fifth Circuit affirmed the bankruptcy court’s conclusion that this was a fraudulent transfer: “When it became clear that Mr. Wiggains would file bankruptcy to satisfy his outstanding debts, the couple entertained various options and made their best estimate on ultimate financial benefits by having only Mr. Wiggains file after the Partition Agreement was recorded. Allowing Mrs. Wiggains to sidestep the statutory limits for homestead exemptions and obtain approximately $500,000 in proceeds that otherwise are for creditors would lay waste to the provisions of the Bankruptcy Code involved here.” Wiggains v. Reed, No. 15-11249 (Feb. 14, 2017).
 Texas Lawyer reports that six candidates are under consideration for the two vacancies on the Fifth Circuit – “Texas Supreme Court Justice Don Willett; U.S. District Court Judge Reed O’Connor of Fort Worth; former Texas solicitor general James Ho; Andy Oldham, a deputy general counsel to Gov. Greg Abbott; Michael Massengale, a justice on Houston’s First Court of Appeals; and Brett Busby, a justice on Houston’s Fourteenth Court of Appeals” – the full story appears here.
Texas Lawyer reports that six candidates are under consideration for the two vacancies on the Fifth Circuit – “Texas Supreme Court Justice Don Willett; U.S. District Court Judge Reed O’Connor of Fort Worth; former Texas solicitor general James Ho; Andy Oldham, a deputy general counsel to Gov. Greg Abbott; Michael Massengale, a justice on Houston’s First Court of Appeals; and Brett Busby, a justice on Houston’s Fourteenth Court of Appeals” – the full story appears here.
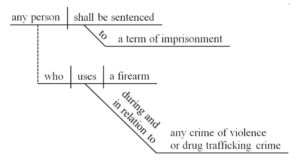 Press coverage of Judge Neil Gorsuch’s nomination to the Supreme Court has noted his intelligent and accessible writing style, including use of a sentence diagram (left) in a criminal case that turned on what elements of the crime
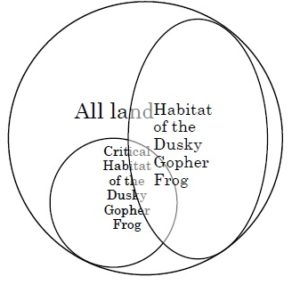
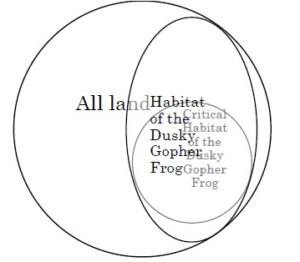
Press coverage of Judge Neil Gorsuch’s nomination to the Supreme Court has noted his intelligent and accessible writing style, including use of a sentence diagram (left) in a criminal case that turned on what elements of the crime  required proof of intent. In the same spirit, in dissent from the denial of en banc rehearing in a highly technical case about protection of the dusky gopher frog (right), Judge Edith Jones used a pair of Venn diagrams to illustrate her view of how the Endangered Species Act should operate (below left), contrasted with the panel opinion’s (below right). Markle Interests v. U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service, No. 14-31008 (Feb. 14, 2017).
required proof of intent. In the same spirit, in dissent from the denial of en banc rehearing in a highly technical case about protection of the dusky gopher frog (right), Judge Edith Jones used a pair of Venn diagrams to illustrate her view of how the Endangered Species Act should operate (below left), contrasted with the panel opinion’s (below right). Markle Interests v. U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service, No. 14-31008 (Feb. 14, 2017).
 CitiMortgage sought to foreclose on Maldonado’s home; in the subsequent litigatoin, it offered summary judgment evidence that he owed a balance of $533,960.80. In response, Maldonado “disputed the amounts that CitiMortgage claimed in attorneys’ fees, inspection fees, escrow, taxes, and late charges,” but did “not provide any evidence of what the correct amounts should be.” Maldonado v. CitiMortgage, No. 16-20541 (Jan. 23, 2017, unpublished).
CitiMortgage sought to foreclose on Maldonado’s home; in the subsequent litigatoin, it offered summary judgment evidence that he owed a balance of $533,960.80. In response, Maldonado “disputed the amounts that CitiMortgage claimed in attorneys’ fees, inspection fees, escrow, taxes, and late charges,” but did “not provide any evidence of what the correct amounts should be.” Maldonado v. CitiMortgage, No. 16-20541 (Jan. 23, 2017, unpublished).
 The issue in United States ex rel. Vavra v. Kellogg Brown & Root, Inc. was whether KBR was liable for kickbacks taken by two employees. The Fifth Circuit held that the answer is fact-specific: “[T]he proper test for imputing knowledge under [the AKA] is that corporations are liable ‘only for the knowing violations of those employees whose authority, responsibility, or managerial role within the corporation is such that their knowledge is imputable to the corporation.'” As for the effect of the alleged kickback, even though “[i]t is true that the district court did not make any findings as to particular service problems [the employee] intended to influence in an improper manner through his gratuities . . . it is enough to connect the gratuity with the specific kind of treatment sought in a way that establishes impropriety,” which was done here “[b]ecause of the nature of the treatment [the employee] sought.” No. 15-41623 (Feb. 3, 2017).
The issue in United States ex rel. Vavra v. Kellogg Brown & Root, Inc. was whether KBR was liable for kickbacks taken by two employees. The Fifth Circuit held that the answer is fact-specific: “[T]he proper test for imputing knowledge under [the AKA] is that corporations are liable ‘only for the knowing violations of those employees whose authority, responsibility, or managerial role within the corporation is such that their knowledge is imputable to the corporation.'” As for the effect of the alleged kickback, even though “[i]t is true that the district court did not make any findings as to particular service problems [the employee] intended to influence in an improper manner through his gratuities . . . it is enough to connect the gratuity with the specific kind of treatment sought in a way that establishes impropriety,” which was done here “[b]ecause of the nature of the treatment [the employee] sought.” No. 15-41623 (Feb. 3, 2017).
 Foster sued about a foreclosure; the state court granted a TRO (so no foreclosure occurred); and the mortgage servicer defendants removed and obtained summary judgment. Foster challenged the denial of her motion to remand, arguing that she did not improperly join the substitute trustee appointed to conduct the foreclosure sale. The Fifth Circuit affirmed: “[B]reach of a trustee’s duty does not constitute an independent tort; rather, it yields a cause of action for wrongful foreclosure. A claim of wrongful foreclosure cannot succeed, however, when no foreclosure has occurred.” Foster v. Deutsche Bank, No. 16-11045 (Feb. 8, 2017).
Foster sued about a foreclosure; the state court granted a TRO (so no foreclosure occurred); and the mortgage servicer defendants removed and obtained summary judgment. Foster challenged the denial of her motion to remand, arguing that she did not improperly join the substitute trustee appointed to conduct the foreclosure sale. The Fifth Circuit affirmed: “[B]reach of a trustee’s duty does not constitute an independent tort; rather, it yields a cause of action for wrongful foreclosure. A claim of wrongful foreclosure cannot succeed, however, when no foreclosure has occurred.” Foster v. Deutsche Bank, No. 16-11045 (Feb. 8, 2017).
 A group of real estate companies paid Prime LLC for consulting services. While the contract allowed termination with 60 days notice, the group and Prime agreed to end the contract without using the notice provision. A creditor complained that this termination made a fraudulent transfer, and the Fifth Circuit agreed that the claim was at least facially plausible: “While the value of the notice period lost by failure to adhere to the notice provision remains an issue for further development in the district court, at this stage
A group of real estate companies paid Prime LLC for consulting services. While the contract allowed termination with 60 days notice, the group and Prime agreed to end the contract without using the notice provision. A creditor complained that this termination made a fraudulent transfer, and the Fifth Circuit agreed that the claim was at least facially plausible: “While the value of the notice period lost by failure to adhere to the notice provision remains an issue for further development in the district court, at this stage  we think the notice requirement secured measurable economic benefit to Prime. Assuming the facts alleged surrounding this transaction to be true, as we must under Rule 12(b)(6), Plaintiff has alleged an asset, cognizable as such under TUFTA, that was constructively transferred.” Hometown 2006-1 1925 Valley View LLC v. Prime Income Asset Management LLC, No. 15-10881 (Feb. 2, 2017)
we think the notice requirement secured measurable economic benefit to Prime. Assuming the facts alleged surrounding this transaction to be true, as we must under Rule 12(b)(6), Plaintiff has alleged an asset, cognizable as such under TUFTA, that was constructively transferred.” Hometown 2006-1 1925 Valley View LLC v. Prime Income Asset Management LLC, No. 15-10881 (Feb. 2, 2017)
On Dallas’s Fox 4 News, following the lead of the Matrix movies, I characterize the nominee as “Scalia Reloaded”:
 Defendants removed, the plaintiff moved to remand, and the the district court granted the motion. It found a waiver of the right to remove, noting this contract provision: “The Parties hereto hereby irrevocably and unconditionally consent to the sole and exclusive jurisdiction of the courts of Harris County in the State of Texas for any action, suit or proceeding arising out of or relating to this Agreement or the Proposed Transaction . . . .” The defendants claimed ambiguity (which would make the waiver no longer be “clear and unambiguous,” and thus not satisfy the demanding standard in this area) from (1) the definition of “Proposed Transaction,” (2) the definitions of the relevant parties, and the use of “Proposed Transaction” in the above part of the relevant clause, but not in another, similar provision later in it. The Fifth Circuit rejected these arguments and affirmed, but also affirmed the denial of any award of attorneys’ fees. Grand View PV Solar Two, LLC v. Helix Elec., Inc., No. 16-20384 (Feb. 1, 2017). The opinion is a good summary of the law on this topic, which has not been addressed in detail recently.
Defendants removed, the plaintiff moved to remand, and the the district court granted the motion. It found a waiver of the right to remove, noting this contract provision: “The Parties hereto hereby irrevocably and unconditionally consent to the sole and exclusive jurisdiction of the courts of Harris County in the State of Texas for any action, suit or proceeding arising out of or relating to this Agreement or the Proposed Transaction . . . .” The defendants claimed ambiguity (which would make the waiver no longer be “clear and unambiguous,” and thus not satisfy the demanding standard in this area) from (1) the definition of “Proposed Transaction,” (2) the definitions of the relevant parties, and the use of “Proposed Transaction” in the above part of the relevant clause, but not in another, similar provision later in it. The Fifth Circuit rejected these arguments and affirmed, but also affirmed the denial of any award of attorneys’ fees. Grand View PV Solar Two, LLC v. Helix Elec., Inc., No. 16-20384 (Feb. 1, 2017). The opinion is a good summary of the law on this topic, which has not been addressed in detail recently.
The receiver of the Allen Stanford businesses sued several investors for receiving fraudulent conveyances. In earlier appeals, the Fifth Circuit resolved other thresehold issues in these cases; in Janvey v. Alguire, the Court reviewed the denials of the defendants’ motions to compel arbitration. It affirmed, rejecting their arguments based on arbitration clauses in various Stanford-related documents: “Because the Receiver may sue on behalf of any of the Stanford entities that has a claim against the defendants, becausehe has chosen to sue on behalf of the Bank, which has not consented to arbitrate claims against any of the defendants [except for one, who waived the issue], and because none of the equitable doctrines urged by the defendants applies, the Receiver cannot be compelled to arbitate his claims against these defendants.” No. 14-10945 et al. (Jan. 31, 2017).
defendants, becausehe has chosen to sue on behalf of the Bank, which has not consented to arbitrate claims against any of the defendants [except for one, who waived the issue], and because none of the equitable doctrines urged by the defendants applies, the Receiver cannot be compelled to arbitate his claims against these defendants.” No. 14-10945 et al. (Jan. 31, 2017).